| Revision History | ||
|---|---|---|
| Revision 1.8 | 2022 April 20 | jbs |
| Add CABB block reboot figure back into the troubleshooting section. | ||
| Revision 1.7 | 2021 October 19 | jbs |
| Remove link to remote observing web page, and update other links. Changed advice on sampler levels. Fixed description of how CABB calculates delays. Fixed description for heat stow trigger conditions. Split the very long flowchart for the printed output. Remove info on how to configure Twitter for SMS, since that is no longer available. | ||
| Revision 1.6 | 2018 June 21 | jfk, ghh |
| Substantial updates to content | ||
| Revision 1.5 | 2018 March 15 | jbs |
| Add a section describing unattended observing, and update information on PMon wind stows | ||
| Revision 1.4 | 2016 May 31 | jbs |
| Document how to use the ATCA alarm Twitter feed | ||
| Revision 1.3 | 2015 Nov 24 | jbs |
| Add description of how to set CABB attenuators for 16cm | ||
| Revision 1.2 | 2015 Oct 23 | rmw, sb, klw |
| Substantial revision of content and layout | ||
| Revision 1.1 | 2014 Jul 09 | rmw |
| Substantial revision of content and layout | ||
| Revision 1.0 | 2014 Mar 20 | jbs |
| Initial Docbook revision | ||
This chapter describes the steps necessary to observe with the ATCA. It assumes that observing strategy has been determined and schedule files created. See Chapter 2 for information on determining observing strategy and Section 2.3 for information on creating schedule files.
In general, observing takes place in the SOC in Marsfield. It is possible to remote observe from anywhere with adequate network and phone connectivity.
We are currently in the process of creating ATCA Tutorial videos that are available on our YouTube channel. These videos are intended to help new observers familiarise themselves with the various applications and operational processes related to the ATCA and are provided as “refresher courses” for more experienced observers.
Observers are responsible for the collection of their own data and appropriate checks to ensure the quality of the data. They are also expected to ensure the safety of the array (to the best of their ability). This is always secondary to any personal safety concerns.
An ATNF staff astronomer or student is rostered to support observers with setting up and training new observers to use the array (the Duty Astronomer or DA). The DA should be the first point of call if there are problems or queries with observations.
The steps to observe with the compact array are:
connect to VNC sessions and prepare for observing (Section 3.1)
taking control from the previous observer (Section 3.2)
set up and calibrate the array (Section 3.3)
observe target source(s) (Section 3.4)
monitor observations for problems (Section 3.5)
end observations
When observing remotely, getting connected can take a while so observers should make sure that they leave plenty of time before their observing block begins.
Before the start of observations, observers need to log into the ATCA Portal.
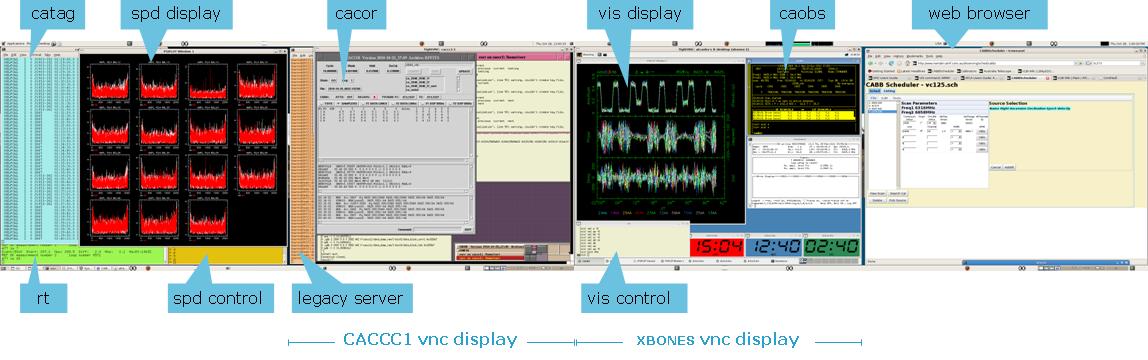
Two VNC sessions are set up for control of the array:
The xbones session runs caobs, vis and assistance.
The caccc1 session runs tasks associated with the correlator.
Remote observers should connect to both of these VNC sessions before the start of observations. See for information on setting up remote observations (In Marsfield the necessary windows are already set up on Ara in the SOC, along with a number of additional windows with supplementary information and observing tasks.)